Virtual DOM 模型
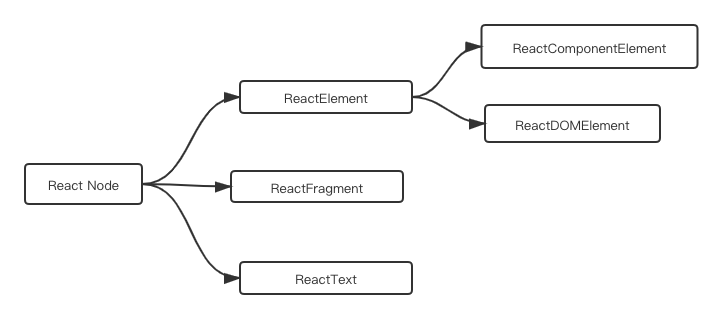
ReactNode 中不同类型节点所需要的基础元素:
type ReactNode = ReactElement | ReactFragment | ReactText;
type ReactElement = ReactComponentElement | ReactDOMElement;
type ReactDOMElement = {
type: string,
props: {
children: ReactNodeList,
className: string,
// etc...
},
key: string | boolean | number | null,
ref: string | null
};
type ReactComponentElement<TProps> = {
type: ReactClass<TProps>,
props: TProps,
key: string | boolean | number | null,
ref: string | null
};
type ReactFragment = Array<ReactNode | ReactEmpty>;
type ReactNodeList = ReactNode | ReactEmpty;
type ReactText = string | number;
type ReactEmpty = null | undefined | boolean;
创建React元素
const app = <Nav color="blue"><Profile>click</Profile></Nav>;
// 输出(JavaScript):
const app = React.createElement(
Nav,
{color:"blue"},
React.createElement(Profile, null, "click")
);
通过 JSX 创建的虚拟元素最终会被编译成调用 React 的 createElement 方法。那么 createElement 方法到底做了什么?
// createElement 只是做了简单的参数修正,返回一个 ReactElement 实例对象,
// 也就是虚拟元素的实例
ReactElement.createElement = function (type, config, children) {
// 初始化参数
var propName;
var props = {};
var key = null;
var ref = null;
var self = null;
var source = null;
// 如果存在 config,则提取里面的内容
if (config != null) {
ref = config.ref === undefined ? null : config.ref;
key = config.key === undefined ? null : '' + config.key;
self = config.__self === undefined ? null : config.__self;
source = config.__source === undefined ? null : config.__source;
// 复制 config 里的内容到 props(如 id 和 className 等)
for (propName in config) {
if (config.hasOwnProperty(propName) &&
!RESERVED_PROPS.hasOwnProperty(propName)) {
props[propName] = config[propName];
}
}
}
// 处理 children,全部挂载到 props 的 children 属性上。如果只有一个参数,直接赋值给 children,
// 否则做合并处理
var childrenLength = arguments.length - 2;
if (childrenLength === 1) {
props.children = children;
} else if (childrenLength > 1) {
var childArray = Array(childrenLength);
for (var i = 0; i < childrenLength; i++) {
childArray[i] = arguments[i + 2];
}
props.children = childArray;
}
// 如果某个 prop 为空且存在默认的 prop,则将默认 prop 赋给当前的 prop
if (type && type.defaultProps) {
var defaultProps = type.defaultProps;
for (propName in defaultProps) {
if (typeof props[propName] === 'undefined') {
props[propName] = defaultProps[propName];
}
}
}
// 返回一个 ReactElement 实例对象
return ReactElement(type, key, ref, self, source, ReactCurrentOwner.current, props);
};
初始化组件入口
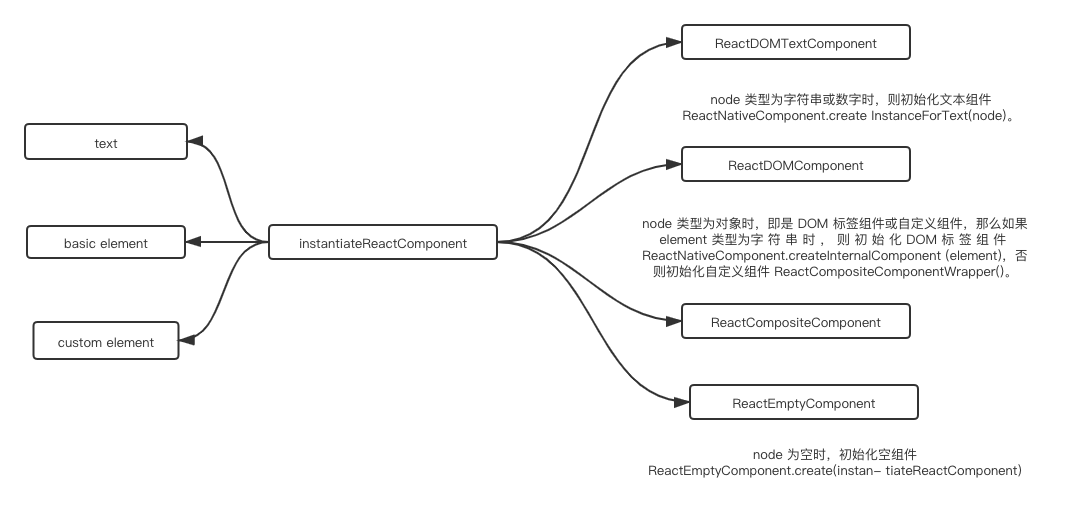
当使用 React 创建组件时,首先会调用 instantiateReactComponent,这是初始化组件的入口函数,它通过判断 node 类型来区分不同组件的入口。
// 初始化组件入口 var instance;
function instantiateReactComponent (node, parentCompositeType) {
// 空组件(ReactEmptyComponent)
if (node === null || node === false) {
instance = ReactEmptyComponent.create(instantiateReactComponent);
}
if (typeof node === 'object') {
var element = node;
if (typeof element.type === 'string') {
// DOM标签(ReactDOMComponent)
instance = ReactNativeComponent.createInternalComponent(element);
} else if (isInternalComponentType(element.type)) {
// 不是字符串表示的自定义组件暂无法使用,此处将不做组件初始化操作
instance = new element.type(element);
} else {
// 自定义组件(ReactCompositeComponent)
instance = new ReactCompositeComponentWrapper();
}
} else if (typeof node === 'string' || typeof node === 'number') { // 字符串或数字(ReactTextComponent)
instance = ReactNativeComponent.createInstanceForText(node);
} else {
// 不做处理
}
// 设置实例 instance.construct(node);
// 初始化参数 instance._mountIndex = 0; instance._mountImage = null;
return instance;
}
文本组件
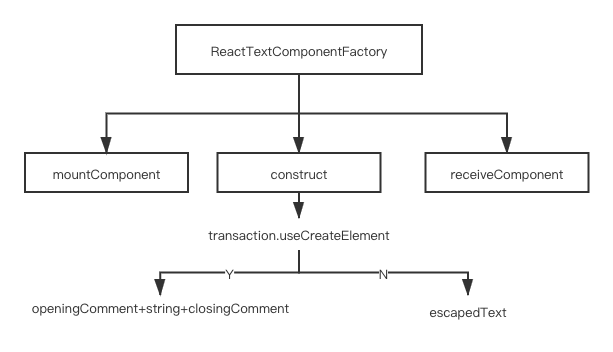
当 node 类型为文本节点时是不算 Virtual DOM 元素的,但 React 为了保持渲染的一致性,将其封装为文本组件 ReactDOMTextComponent。
在执行 mountComponent 方法时,ReactDOMTextComponent 通过 transaction.useCreateElement 判断该文本是否是通过 createElement 方法创建的节点,如果是,则为该节点创建相应的标签和标识 domID,这样每个文本节点也能与其他 React 节点一样拥有自己的唯一标识,同时也拥有了 Virtual DOM diff 的权利。但如果不是通过 createElement 创建的文本,React 将不再为其创建 <span>(React 15.0 不再为裸露的文本内容包裹 <span> 标签) 和 domID 标识,而是直接返回文本内容。
在执行 receiveComponent 方法时,可以通过 DOMChildrenOperations.replaceDelimitedText(commentNodes[0], commentNodes[1], nextStringText) 来更新文本内容。
DOM 标签组件
React 的 <div> 并不是原生 <div> 标签,它其实是 React 生成的 Virtual DOM 对象。Virtual DOM 就如同一个隔离的沙盒,因此 React 的处理并不是直接操作和污染原生 DOM, 这样不仅保持了性能上的高效和稳定,而且降低了直接操作原生 DOM 而导致错误的风险。
ReactDOMComponent 针对 Virtual DOM 标签的处理主要分为以下两个部分:
- 属性的更新,包括更新样式、更新属性、处理事件等;
- 子节点的更新,包括更新内容、更新子节点,此部分涉及 diff 算法。
- 属性更新
当执行 mountComponent 方法时,ReactDOMComponent 首先会生成标记和标签,通过 this.createOpenTagMarkupAndPutListeners(transaction) 来处理 DOM 节点的属性和事件。
如果存在事件,则针对当前的节点添加事件代理,即调用 enqueuePutListener(this, propKey, propValue, transaction)。
如果存在样式,首先会对样式进行合并操作 Object.assign({}, props.style),然后通过 CSSPropertyOperations.createMarkupForStyles(propValue, this) 创建样式。
通过 DOMPropertyOperations.createMarkupForProperty(propKey, propValue) 创建属性。
通过 DOMPropertyOperations.createMarkupForID(this._domID) 创建唯一标识。
当执行 receiveComponent 方法时, ReactDOMComponent 会通过 this.updateComponent (transaction, prevElement, nextElement, context) 来更新 DOM 节点属性。
先是删除不需要的旧属性。如果不需要旧样式,则遍历旧样式集合,并对每个样式进行置空 删除;如果不需要事件,则将其事件监听的属性去掉,即针对当前的节点取消事件代理 deleteListener(this, propKey);如果旧属性不在新属性集合里时,则需要删除旧属性 DOMPropertyOperations.deleteValueForProperty(getNode(this), propKey)。
再是更新新属性。
- 如果存在新样式,则将新样式进行合并 Object.assign({}, nextProp);
- 如果在旧样式中但不在新样式中,则清除该样式;
- 如果既在旧样式中也在新样式中,且不相同,则更新该样式
styleUpdates[styleName] = nextProp[styleName]; - 如果在新样式中,但不在旧样式中,则直接更新为新样式 styleUpdates = nextProp;
- 如果存在事件更新,则添加事件监听的属性
enqueuePutListener(this, propKey, nextProp, transaction); - 如果存在新属性,则添加新属性,或者更新旧的同名属性
DOMPropertyOperations.setValueForAttribute(node, propKey, nextProp)。
至此,ReactDOMComponent 完成了 DOM 节点属性更新的操作。
- 更新子节点
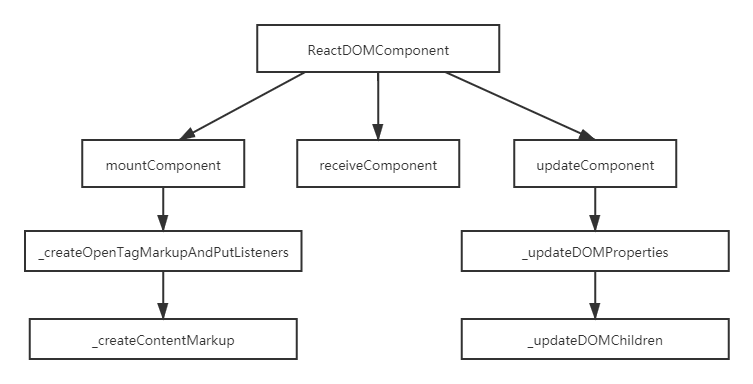
当执行 mountComponent 方法时,ReactDOMComponent 会通过 this._createContentMarkup(transaction, props, context) 来处理 DOM 节点的内容。
首先,获取节点内容 props.dangerouslySetInnerHTML。如果存在子节点,则通过 this.mountChildren(childrenToUse, transaction, context) 对子节点进行初始化渲染:
当执行 receiveComponent 方法时,ReactDOMComponent 会通过 this._updateDOMChildren(lastProps, nextProps, transaction, context) 来更新 DOM 内容和子节点。
先是删除不需要的子节点和内容。如果旧节点存在,而新节点不存在,说明当前节点在更新后被删除,此时执行方法 this.updateChildren(null, transaction, context);如果旧的内容存在,而新的内容不存在,说明当前内容在更新后被删除,此时执行方法 this.updateTextContent('')。
再是更新子节点和内容。如果新子节点存在,则更新其子节点,此时执行方法 this.updateChildren(nextChildren, transaction, context);如果新的内容存在,则更新内容,此时执行方法 this.updateTextContent('' + nextContent)。
至此,ReactDOMComponent 完成了 DOM 子节点和内容的更新操作。
当卸载组件时,ReactDOMComponent 会进行一系列的操作,如卸载子节点、清除事件监听、清空标识等。
自定义组件
ReactCompositeComponent 自定义组件实现了一整套 React 生命周期和 setState 机制,因此自 定义组件是在生命周期的环境中进行更新属性、内容和子节点的操作。这些更新操作与 ReactDOMComponent 的操作类似。